Since the digital revolution began, a large number of online banks, also known as neobanks, have appeared. These have seen tremendous growth in recent years, but as we will see in today’s issue of N5 Insights, sometimes all that glitters is not gold.
Why are the new digital banks losing money? What are the advantages of traditional banks? What is the most successful neobanking sector?
Investors Are Taking an Interest in Fintech and Digital Banks
It is undeniable that in recent times the digital banking and fintech sector has grown by leaps and bounds. We are facing a stage of change, now accelerated by the digitization that the pandemic brought, and both investors and customers are very attentive to this.
Just take a look at the following graph that shows how global investment in fintechs had already reached $ 136 billion by 2019.
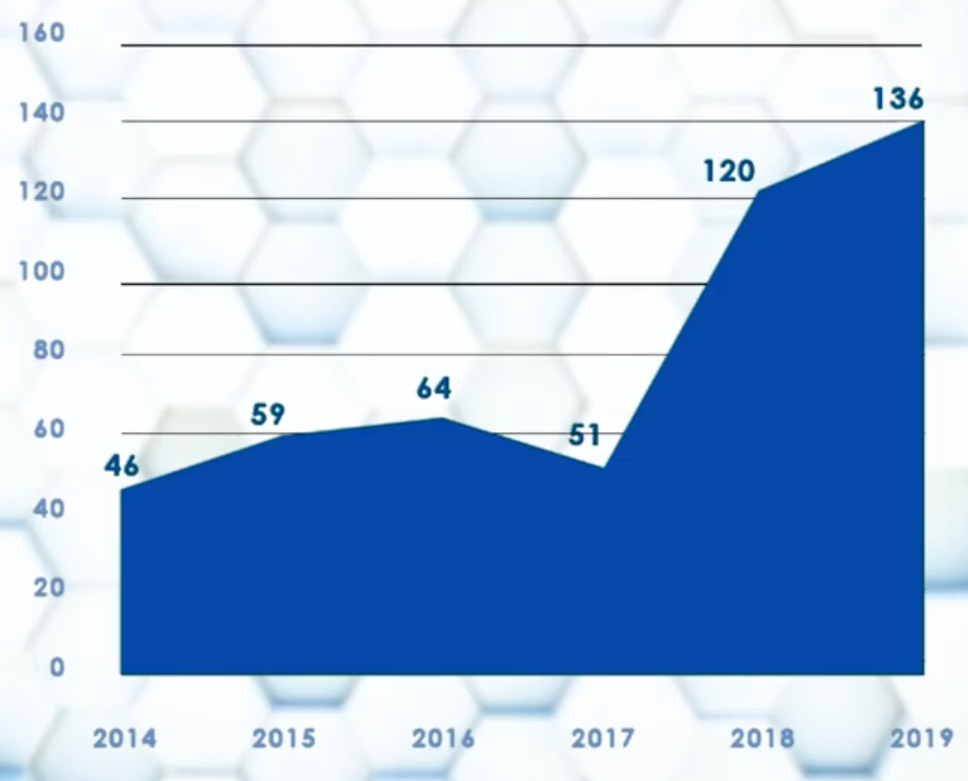
Digital banks have also seen a huge investment surge of late.
It’s no secret that the e-finance industry is growing by leaps and bounds. This is partly due to the convenience of new technologies, but in large part it is also the result of the very rigidity of the banking sector.
European Neobanks Are Losing Money
Digital banks have based their business model around scalability, offering free services, presenting very attractive rates and investing heavily in advertising. And this has worked more than well for them.
In 2020 alone, European neobanks increased their customer base by 150%, while traditional banks only 1%.
Let’s look at the following graph that compares the number of clients of different banks and neobanks.
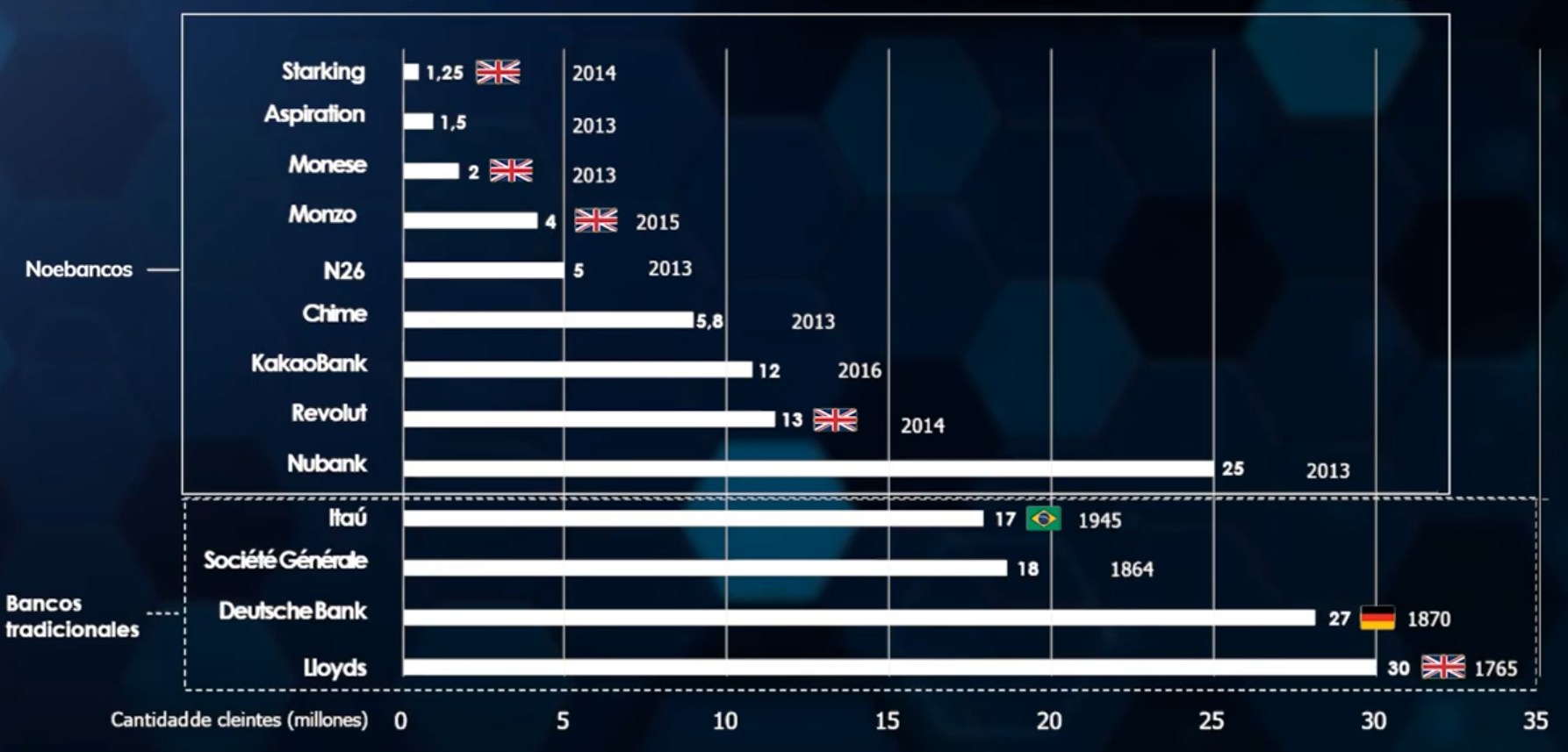
As you can see, above are the neobanks, with companies like Revolut that was founded in 2014 and already has 13 million customers. Compare that to banks that have been operating for hundreds of years like Lloyds (the bottom one), which has just over twice as many customers.
However, it is necessary to stop to make an observation here. Digital banks may be experiencing tremendous growth, but their revenues are not. In fact, it is estimated that each neobank is losing an average of $ 11 USD for each new user.
Why is this happening? Because most of the clients of these new banks either only operate once, or they limit themselves to taking advantage of free services such as ATM withdrawals, without actually contracting any other service.
This means that these banks have a large number of users, but most of them end up not being profitable.
Big Business Is With Traditional Banks
As we have seen recently, even though the new virtual banks are experiencing accelerated growth, this does not necessarily translate into a better business opportunity.
Take for example the portfolio of services. On average for every 5 services offered in traditional banks, neobanks offer 1.5. Not only is it a much smaller offer, but it also generates very little income.
Let’s just take a look at the following graph that compares the earnings of traditional banks with those of digital banks.
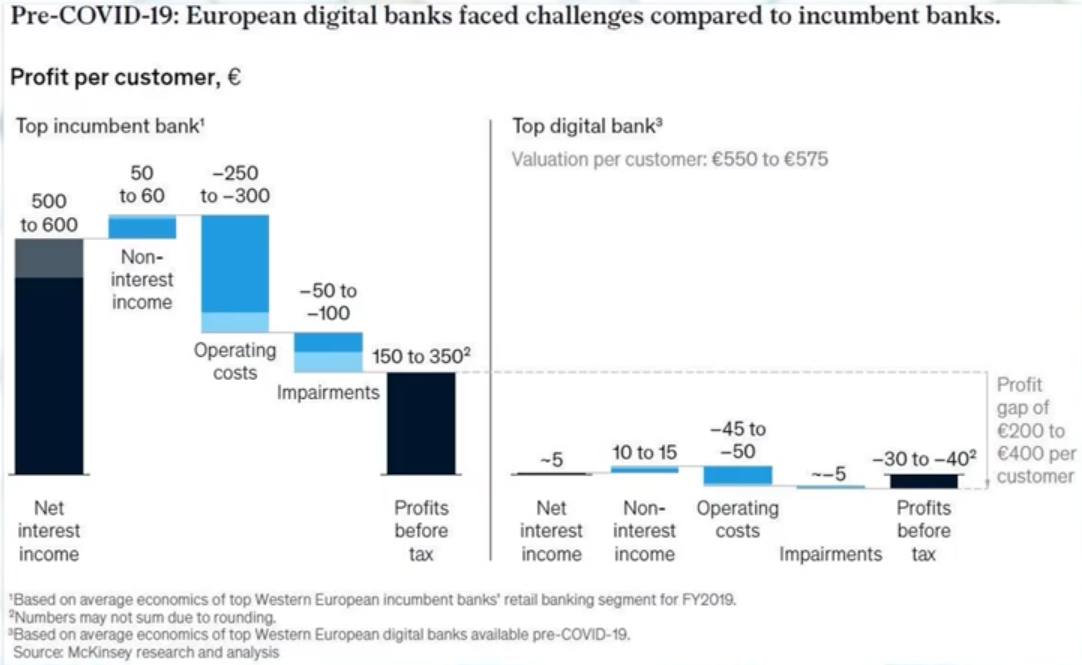
Although the main advantage of neobanks is that by not having physical infrastructure to maintain they do not have as many expenses, when we go to the field of profits we see that these are much lower than those of traditional banks. As the graph shows, this is a margin of € 200 to € 400 per customer.
Confidence Is Still On The Side Of Traditional Banks
While it is true that neobanks are attractive to customers, as we have seen, a large number of users who operate them simply use them once and leave them. Compare this with traditional banks, in which the churn rate is much lower (between 2 – 5%).
The following is a graph showing the results of a survey regarding what reasons would justify people moving from their trusted bank to a neobank.
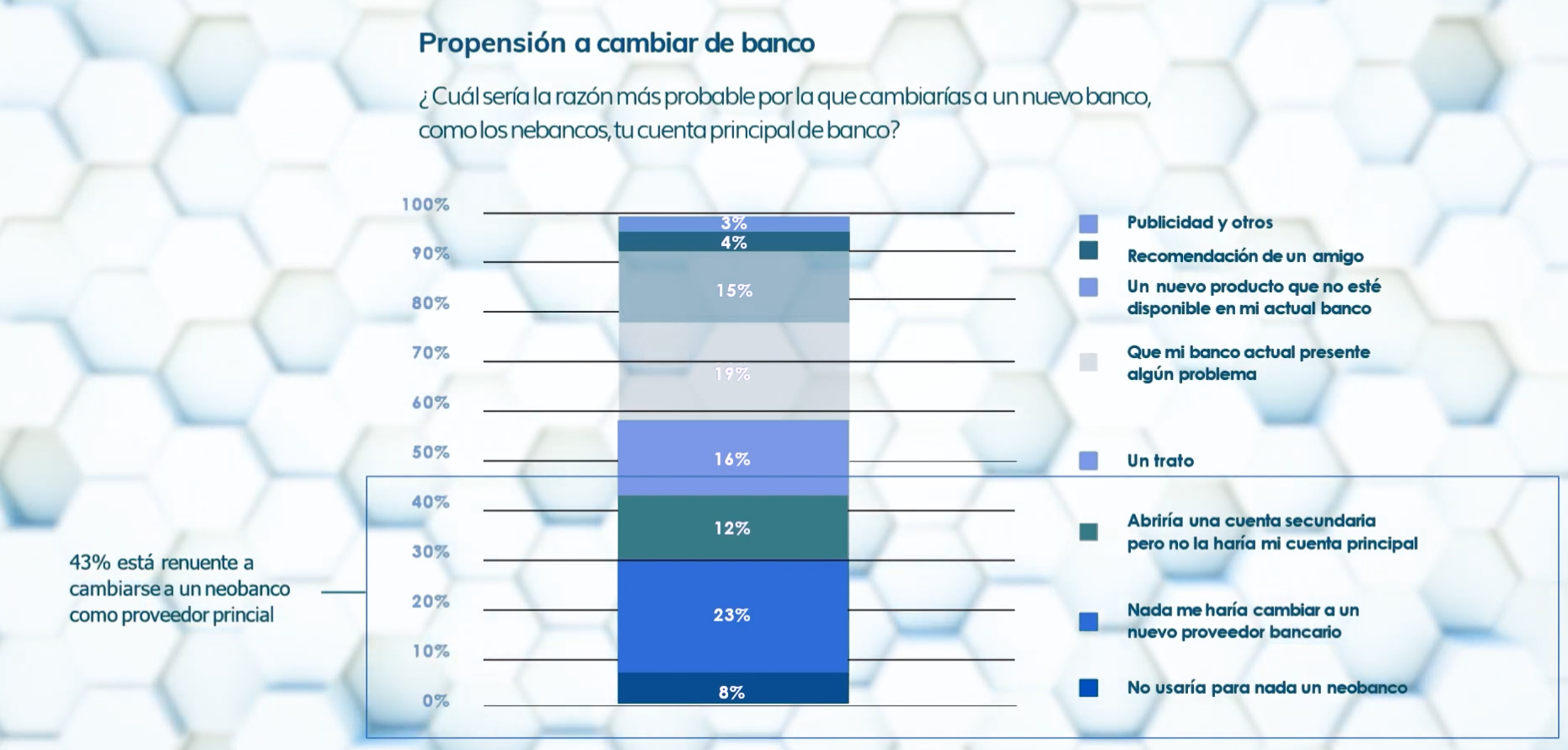
As is marked in the graph, 43% do not directly consider the possibility of moving to a neobank. Meanwhile, 15% would move if they were offered an interesting product that they cannot find in their bank. The problem with this second proposal is clear too: Neo banks simply cannot compete against traditional banks when it comes to offering services.
In other words, people continue to trust traditional banks. They are established institutions – some hundreds of years old.
The Specialized Sector Is Moving Forward
As we have seen, neobanks targeting the general public are not having much success in transforming their users into profitable customers. However, this is not the case when it comes to specialized digital banks.
When it comes to specializing in certain sectors, such as offering financing to small businesses, neobanks are having a great time.
The graph that you will see below shows the money destined to financing for different sectors within the fintech companies.
As the graph points out, a large part of the funding in 2020 went primarily to fintechs offering services for the tech industry. This is followed by payments, and then loans.
Conclusions
As we have seen in this issue of N5 Insights, sometimes all that glitters is not gold. There has been a widespread attempt to replicate startup growth models in the financial industry, but this has not been entirely successful. These are the main points to remember:
- The investment trend continues to revolve around fintech.
- European neobanks have enjoyed rapid growth in recent years, but they are also losing money.
- Traditional banks offer a larger portfolio of services than digital ones in an approximate ratio of 5 to 1.5
- People just keep trusting traditional banks.
- Fintech companies that have specialized in particular sectors have seen better results.
Editorial: Marcelo Frette

