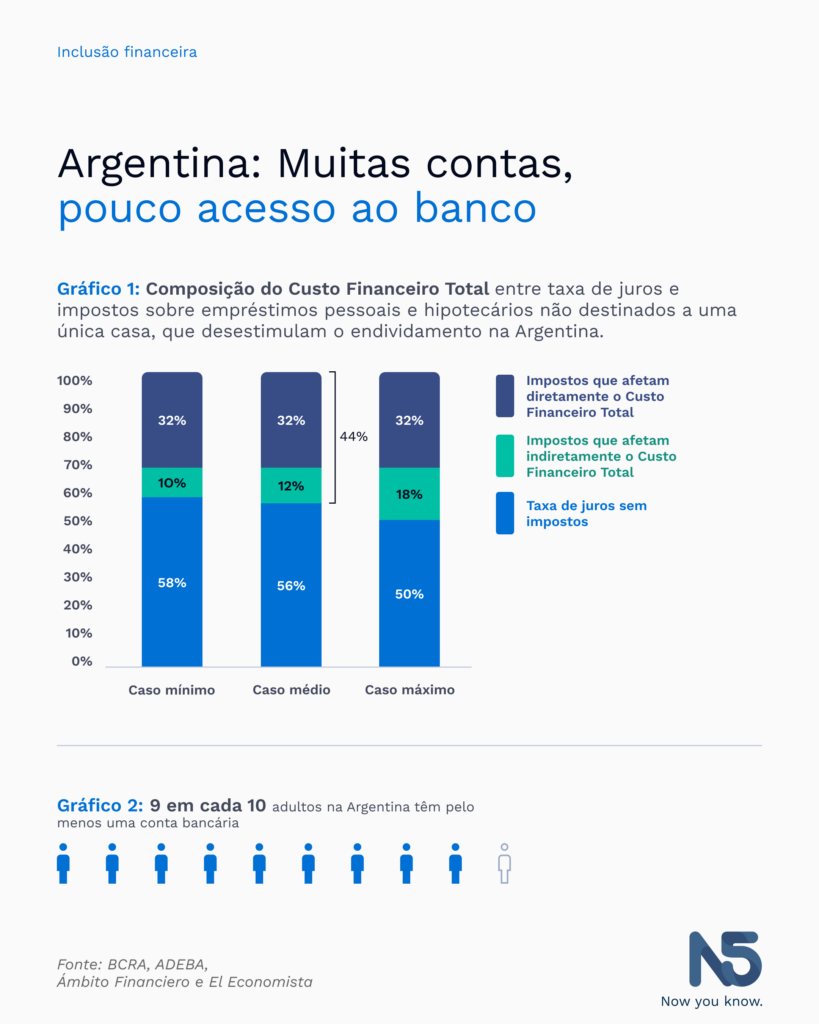
While it may sound optimistic that some reports on Financial Inclusion suggest that 9 out of 10 adults in Argentina have at least one bank account, other studies reveal that the country has the lowest degree of banking in the region. A recent survey of the Association of Argentine Banks (ADEBA) indicates that Argentina has the lowest volume of bank loans and deposits in relation to its GDP. Bank loans represent only 10% of GDP, while the region’s average is 50%.
ADEBA highlights two main factors that explain this low level of bank access in the last 20 years: the instability of the value of the peso and the high tax burden on users of banking services. The entity points out that companies and individuals that use the financial system in Argentina are subject to an excessive national, provincial and municipal tax burden, which is unmatched by other countries in the region. All these taxes and charges make credit and payment operations carried out by bank users more expensive.
In 2021 alone, users of the financial system in Argentina paid $750,000 million in Taxes on Bank Credits and Debits (ICD), which is more than what was collected from import duties, statistical fees, and fuel taxes. A study commissioned by ADEBA to the Mediterranean Foundation reveals that, on average, taxes represent 44% of what is paid when taking out a loan, while the interest rate without taxes represents the remaining 56%. This means that taking loans for production and consumption is penalized and discouraged by the high tax burden of the national, provincial and municipal government.
It is important to analyze how to reduce the tax burden that the government imposes on companies and individuals who take credit and use financial services. Current tax levels are not compatible with a strong bank credit market and broad financial inclusion. To change this situation, it is necessary to define what is the total tax levy on the economy that is compatible with inclusive growth and quality employment, and from there, the government must define its tax policy and assign public spending priorities.

